Your Guide to Taking Medicines Safely as You Get Older
Medicines are designed to help us live longer, healthier lives. However, taking medications incorrectly or mixing certain drugs and supplements can be dangerous. As we age, the likelihood of managing multiple medical conditions increases, which often means taking several medicines. This can raise the risk of side effects. In this article, we’ll explore how to safely take and manage your medications.
What Are Medicines?
Medicines, also known as drugs, are used to prevent or treat diseases and other health conditions. These can be obtained either by prescription or over-the-counter (OTC).
- Prescription Drugs: These are medications you can only get with a doctor’s order, like cholesterol-lowering pills or an asthma inhaler.
- OTC Medicines: These can be purchased without a prescription, such as aspirin or lubricating eye drops.
It’s important to note that dietary supplements are not considered drugs. Instead, they’re meant to maintain or improve health by providing essential vitamins and minerals. For example, calcium and vitamin D supplements can help build strong bones. However, combining prescription drugs, OTC medicines, supplements, or other remedies can sometimes be dangerous. For instance, taking aspirin while on warfarin for heart issues could lead to serious health complications. Always consult with your doctor about all the medications and supplements you take to avoid potential risks.
Starting a New Medicine
Before starting any new prescription, OTC medicine, or supplement, have a conversation with your healthcare provider. Ensure that they are aware of everything else you are taking. Discuss any allergies or previous issues with medications, such as rashes, difficulty breathing, indigestion, dizziness, or mood changes. It’s crucial that your doctor and pharmacist have an updated list of your allergies to avoid prescribing a medicine that could cause an allergic reaction.
You should also ask whether you need to stop or adjust any of your other medications while starting the new one. Mixing new drugs with existing ones can sometimes lead to unpleasant and even dangerous side effects. For example, combining a sedative for sleep and an antihistamine for allergies can impair your reactions, making activities like driving risky.
When you begin a new medication, make a note of the drug’s name, dosage, and why it’s been prescribed. Also, be aware of any special instructions for taking it, which are often included on the prescription label or bottle.
Filling Your Prescription
When you fill your prescriptions, your pharmacist can answer many questions you might have about prescription drugs, OTC medicines, and supplements. Try to have all your prescriptions filled at the same pharmacy so your records are centralized, helping the pharmacist spot potential issues with new drugs.
When filling a prescription, consider the following:
- Patient Profile: Ask if the pharmacy offers a patient profile form. This will keep them informed of all the medications and supplements you’re taking.
- Swallowing Difficulties: If you have trouble swallowing pills, ask if a liquid version is available. Never chew, break, or crush tablets without checking if it will affect the drug’s effectiveness.
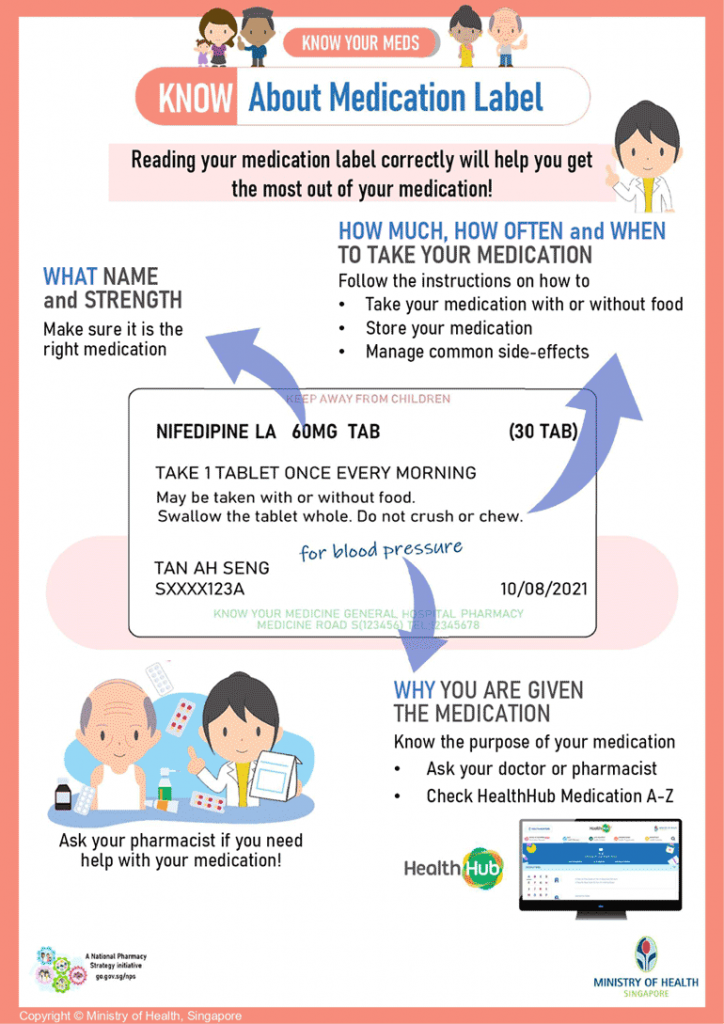
- Label Clarity: Ensure you can read and understand the medication’s name and the directions on the container. If the print is too small, ask for a label with larger type.
- Medication Guides: Many prescriptions come with paper handouts, known as medication guides, that provide essential information to help you avoid serious side effects.
- Container Accessibility: If you struggle to open the container, request an easier-to-open bottle from the pharmacist.
- Storage Instructions: Ask about proper storage. Some medications need to be refrigerated or kept in a specific environment.
- Label Verification: Before leaving the pharmacy, check that the label on your medicine has your name and the correct directions. If it doesn’t, do not take it and consult with the pharmacist.
Understanding Medication Side Effects
Side effects are unwanted or unexpected symptoms that occur when taking medicine. These can range from minor issues like headaches or dry mouth to serious, life-threatening conditions such as severe bleeding or organ damage.
Some side effects may appear when you first start a medication but improve over time. Others may only occur occasionally, while some could persist as long as you are taking the medicine. If you experience uncomfortable side effects, don’t stop taking your medication before consulting with your healthcare provider. It’s important to report any side effects to your doctor or pharmacist so they can help manage them or adjust your treatment plan.
Keeping Track of Your Medicines
Managing multiple medications can be challenging, especially as we age. Here are some tips to help you stay organized:
- Make a List: Write down all the medicines you take, including OTC drugs, vitamins, and supplements. Include the name, dosage, timing, prescribing doctor, and the reason for each medication. Share this list with all your healthcare providers and keep copies at home and in your wallet or purse.
- Familiarize Yourself with Your Medicines: Ensure you can distinguish between your medications by their size, shape, color, or the imprint on the pill.
- Create a File: Keep all the written information that comes with your medicines in a file for easy reference. Retain these guides as long as you’re taking the medication.
- Check Expiration Dates: Never take medicines past their expiration date. Your doctor can advise if you need a refill.
- Secure Your Medicines: Store your medicines out of the reach of children and pets. If you have prescription pain medicines, consider keeping them in a locked cabinet.
- Dispose of Medicines Safely: Dispose of expired or unneeded medications promptly to reduce the risk of accidental ingestion or misuse. Consult your doctor or pharmacist on how to safely discard them, or review the FDA’s guidelines on medication disposal.
Tips for Taking Medicines Safely
Here are some essential tips to ensure you take your medicines safely:
- Follow Instructions: Always read and follow the instructions on medicine labels. Taking more than prescribed can be dangerous, and skipping doses can affect the medicine’s efficacy.
- Set Reminders: Use meals, bedtime, charts, calendars, or smartphone apps to remind you when to take your medicine.
- Turn on a Light: Never take medicine in the dark to avoid mistakes.
- Report Problems: Contact your doctor if you experience any issues with your medications.
- Be Honest: Inform your doctor about your use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs, as they can affect how well your medicines work.
- Ask for Help: Bring a friend or family member to your doctor’s appointments if you need help understanding or remembering medical advice.
- Check Before Stopping: Always finish your prescription or check with your doctor before stopping a medication. Some medicines should only be taken as needed.
- Don’t Share Medications: Never take someone else’s medicine or share yours with others.
By following these guidelines, you can safely manage your medications and maintain your health as you age.
